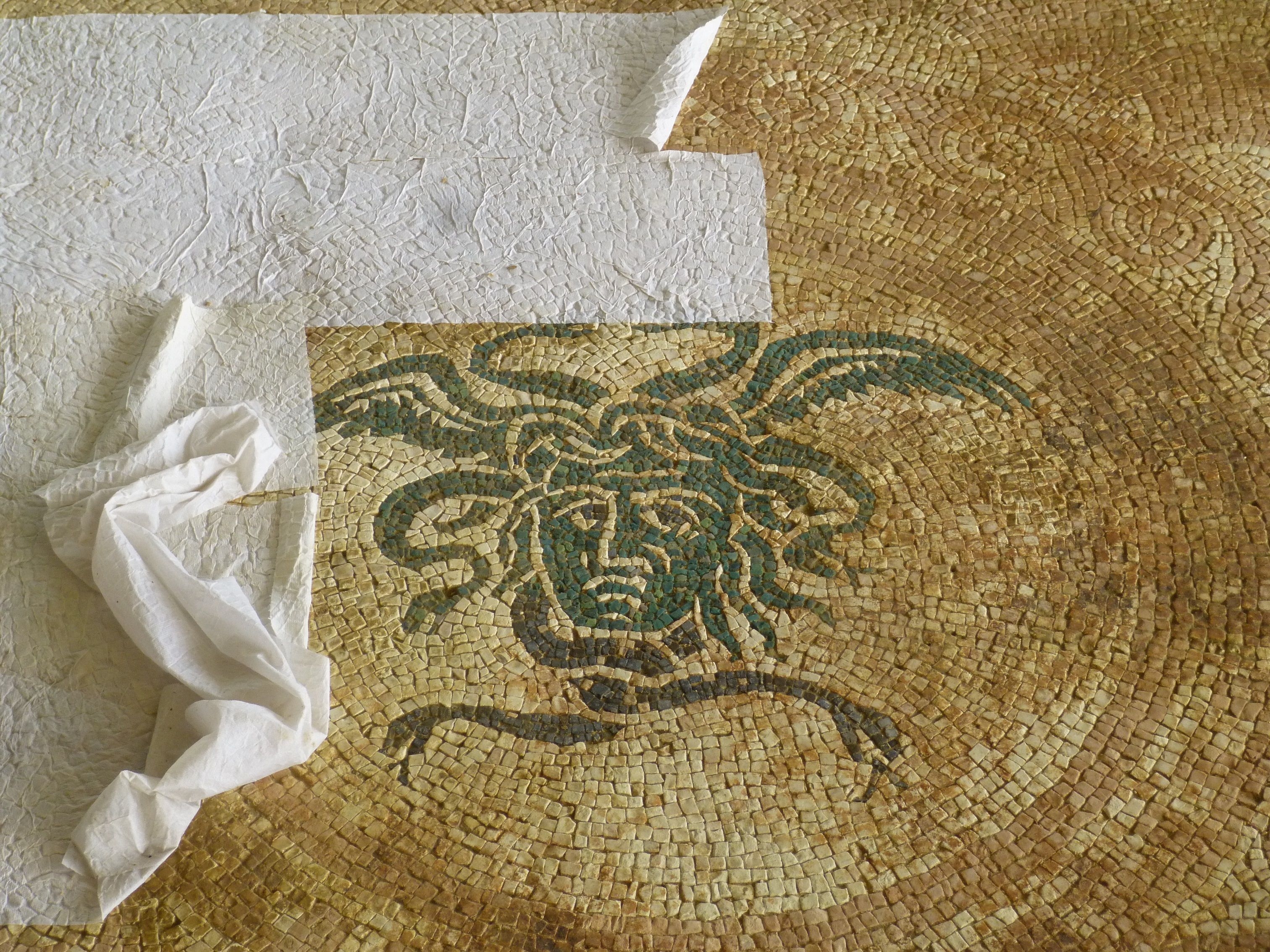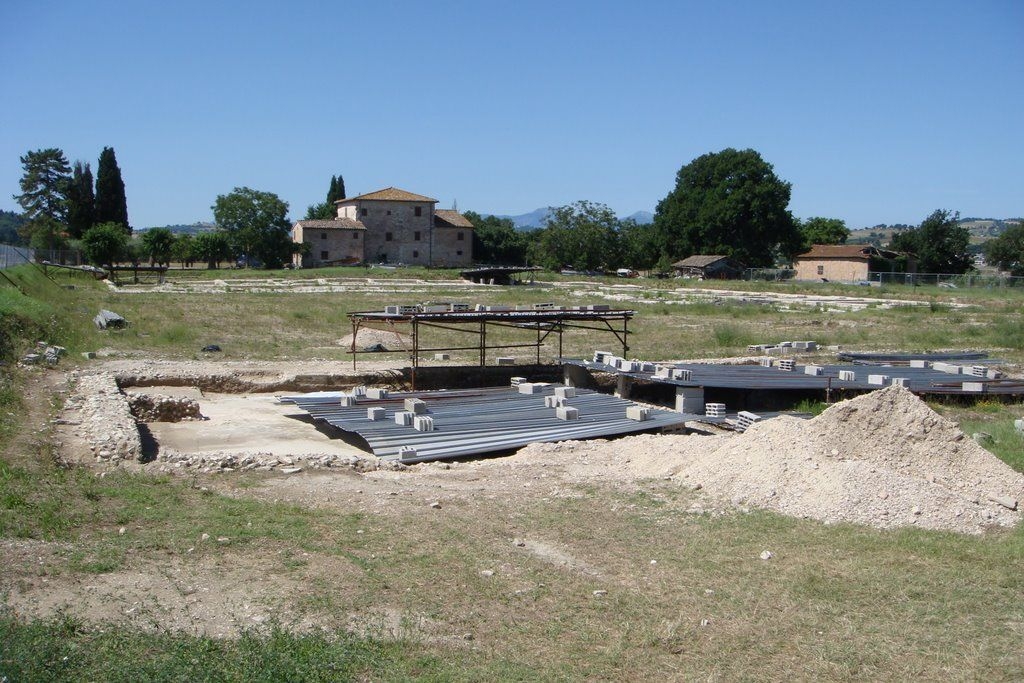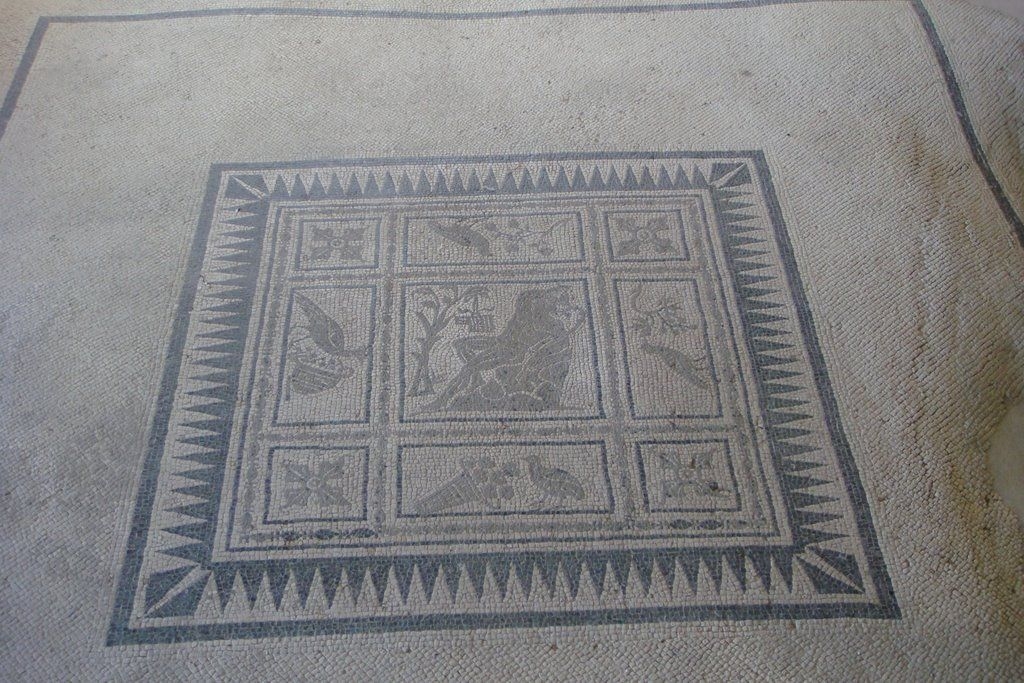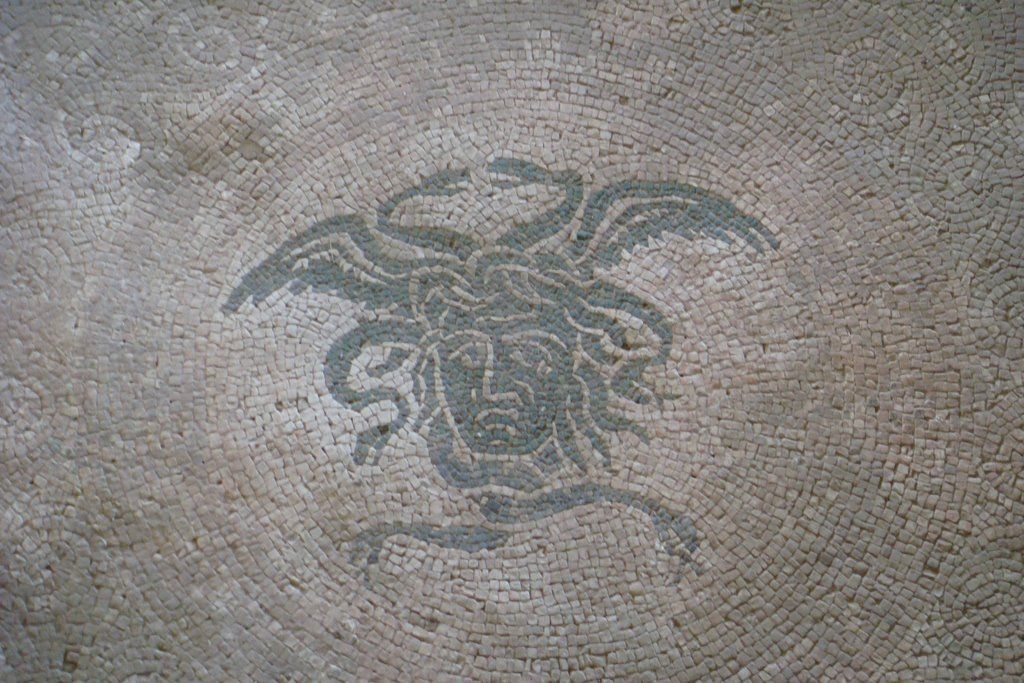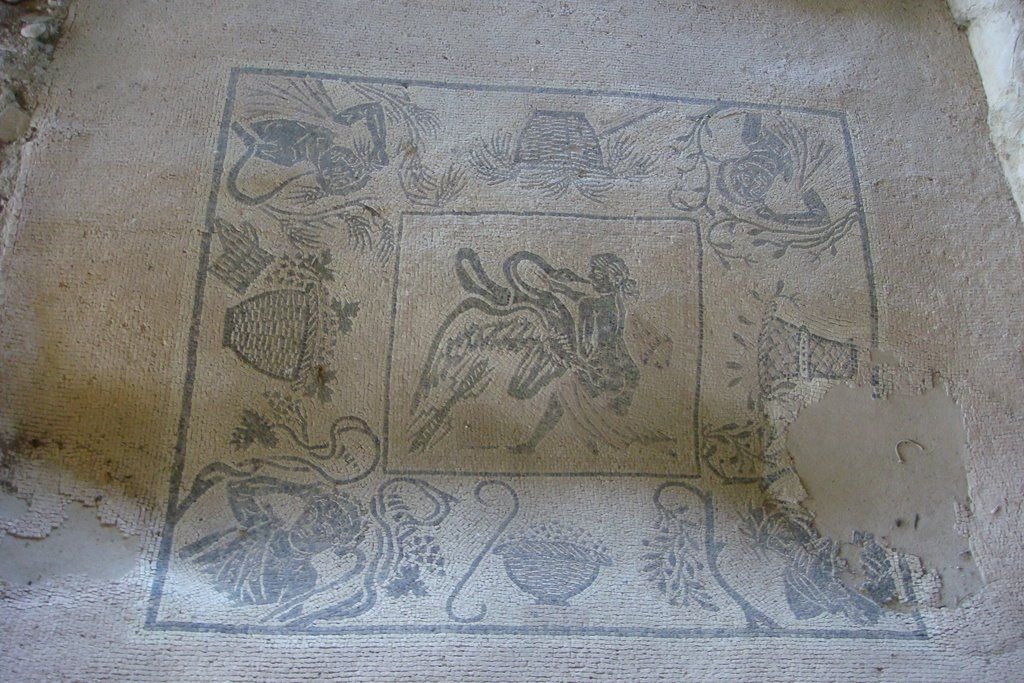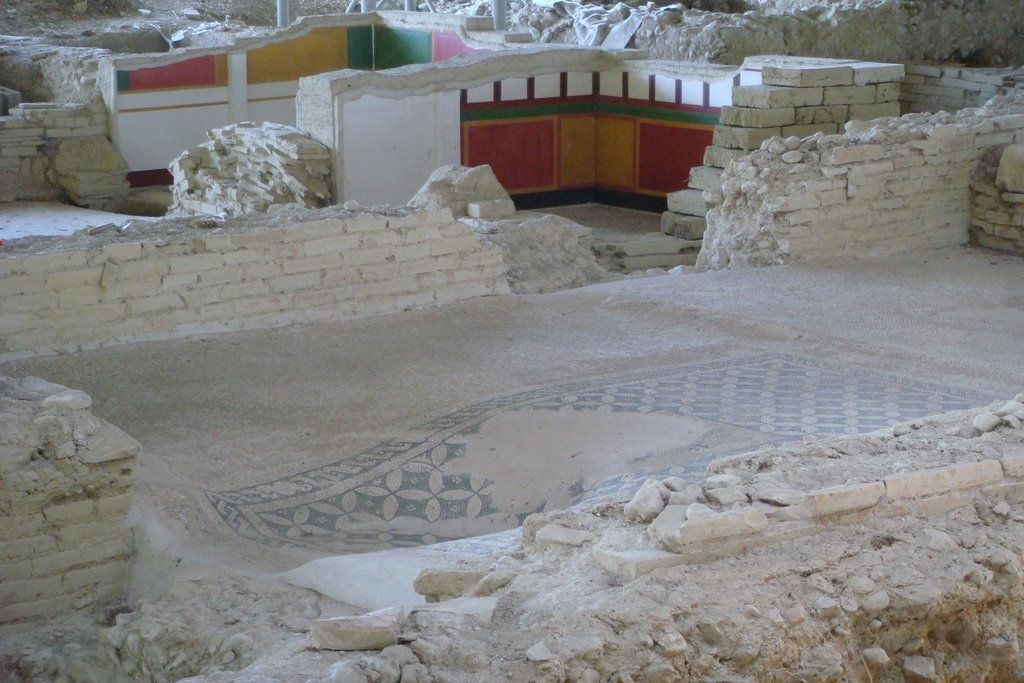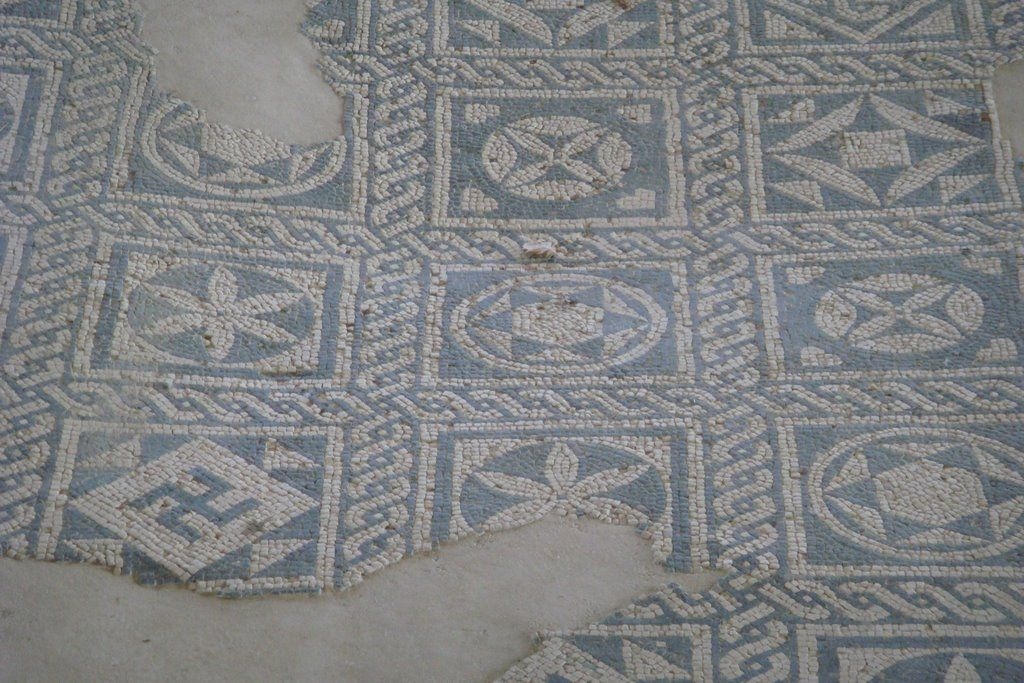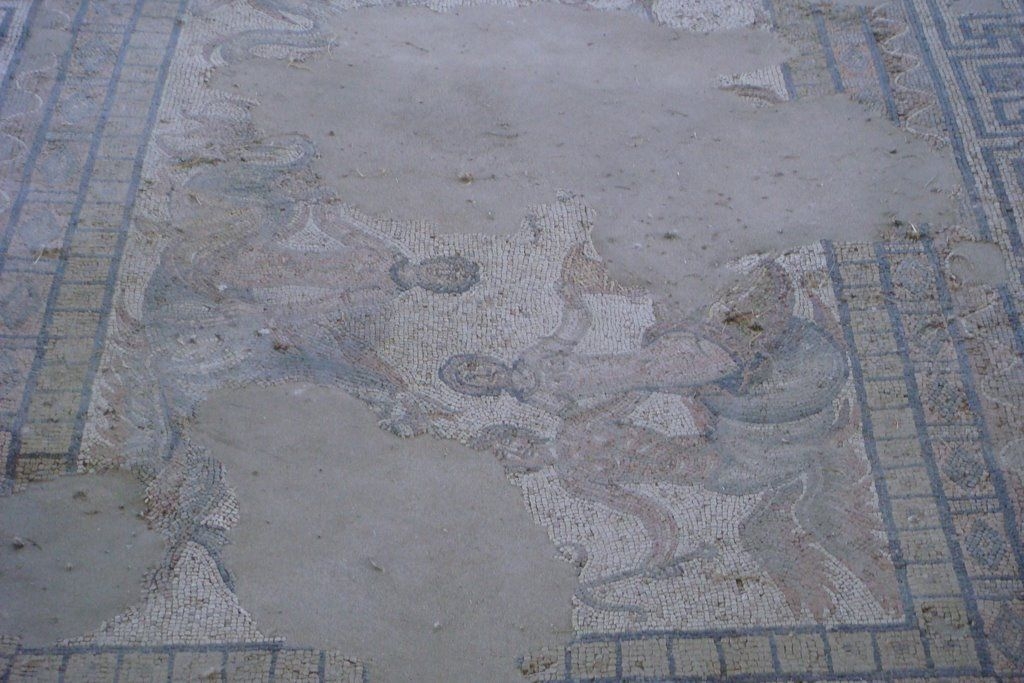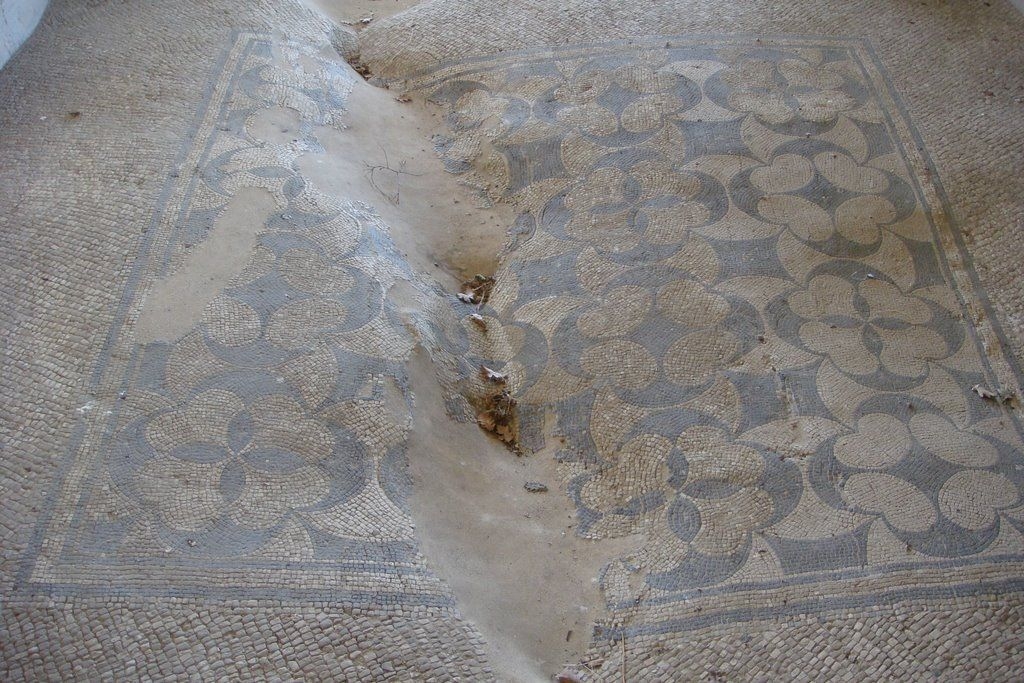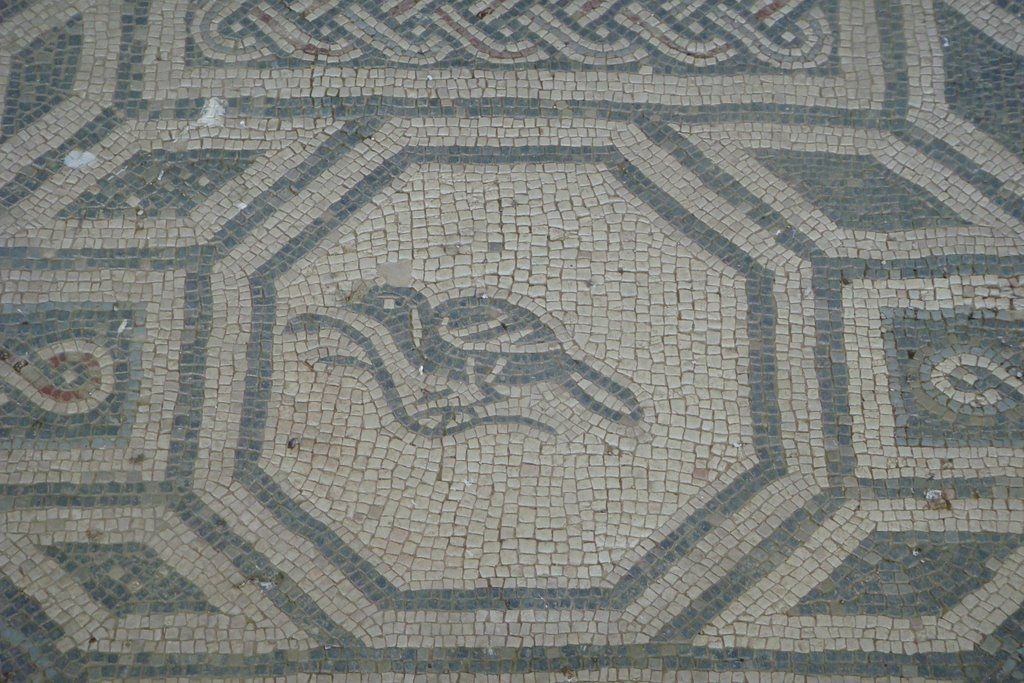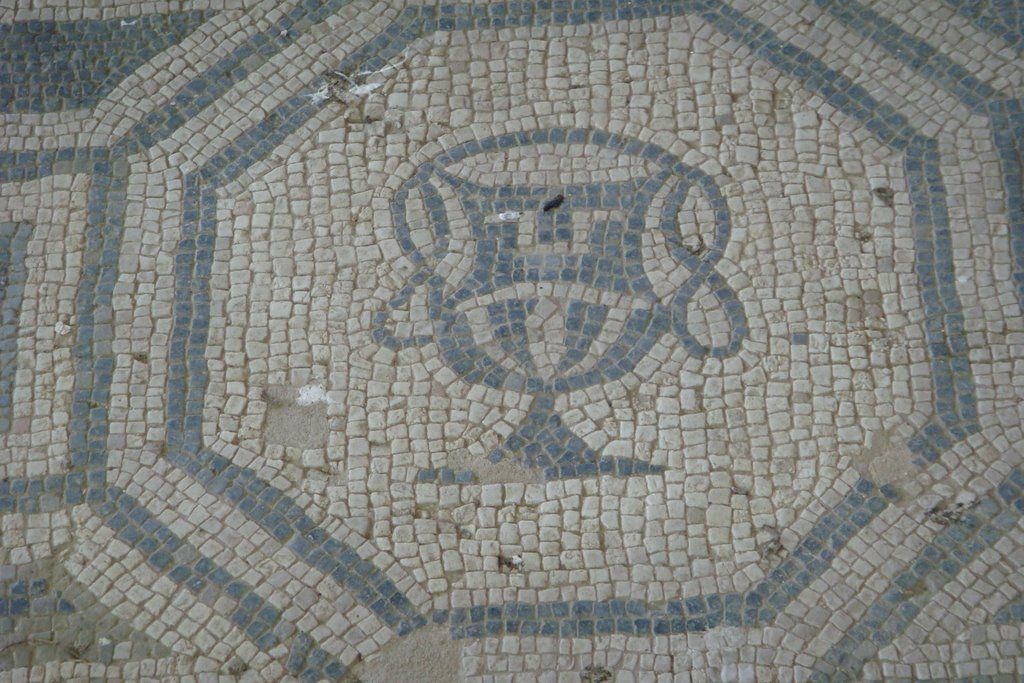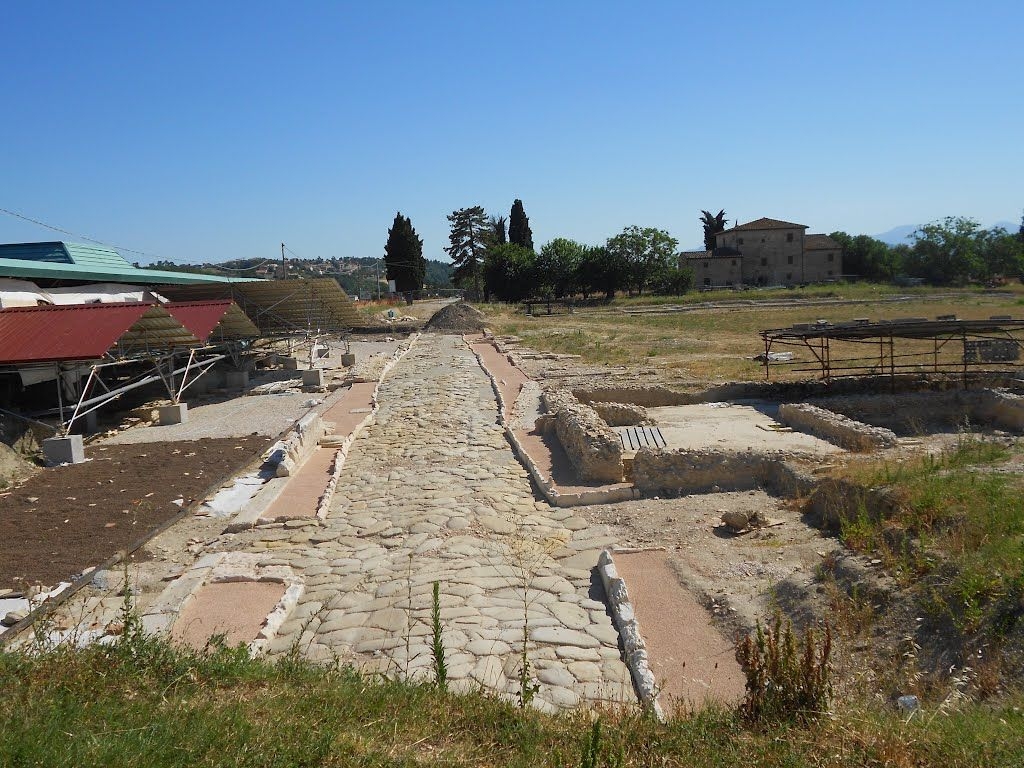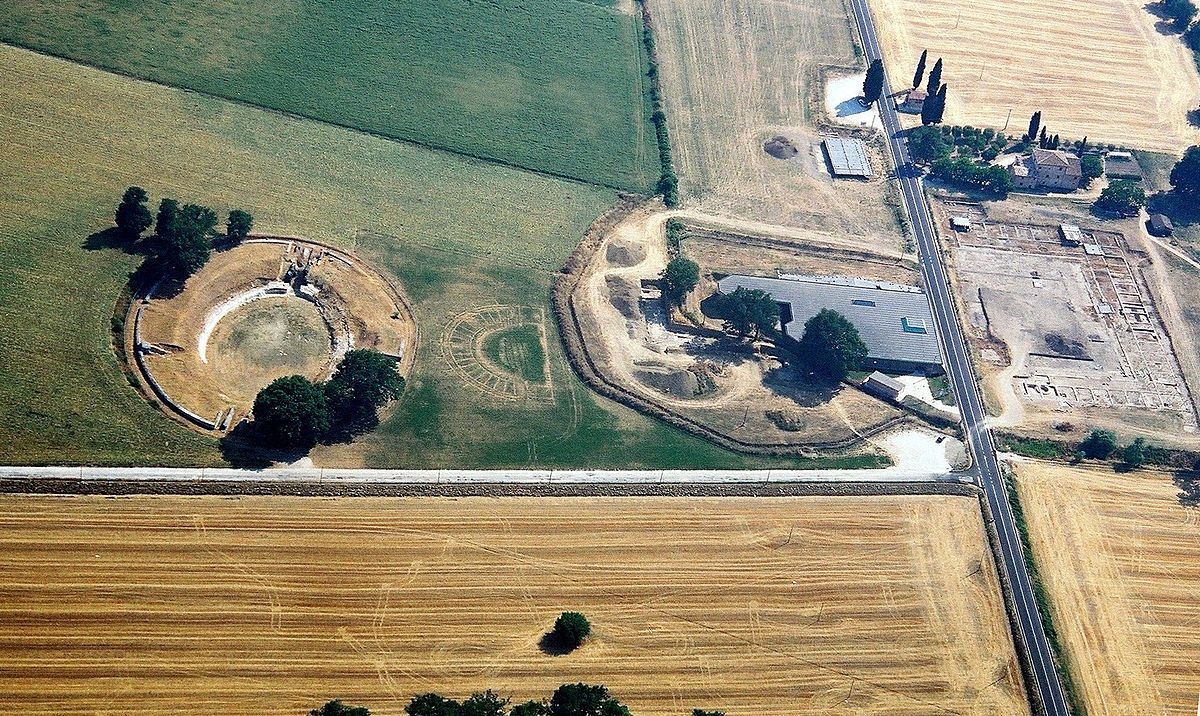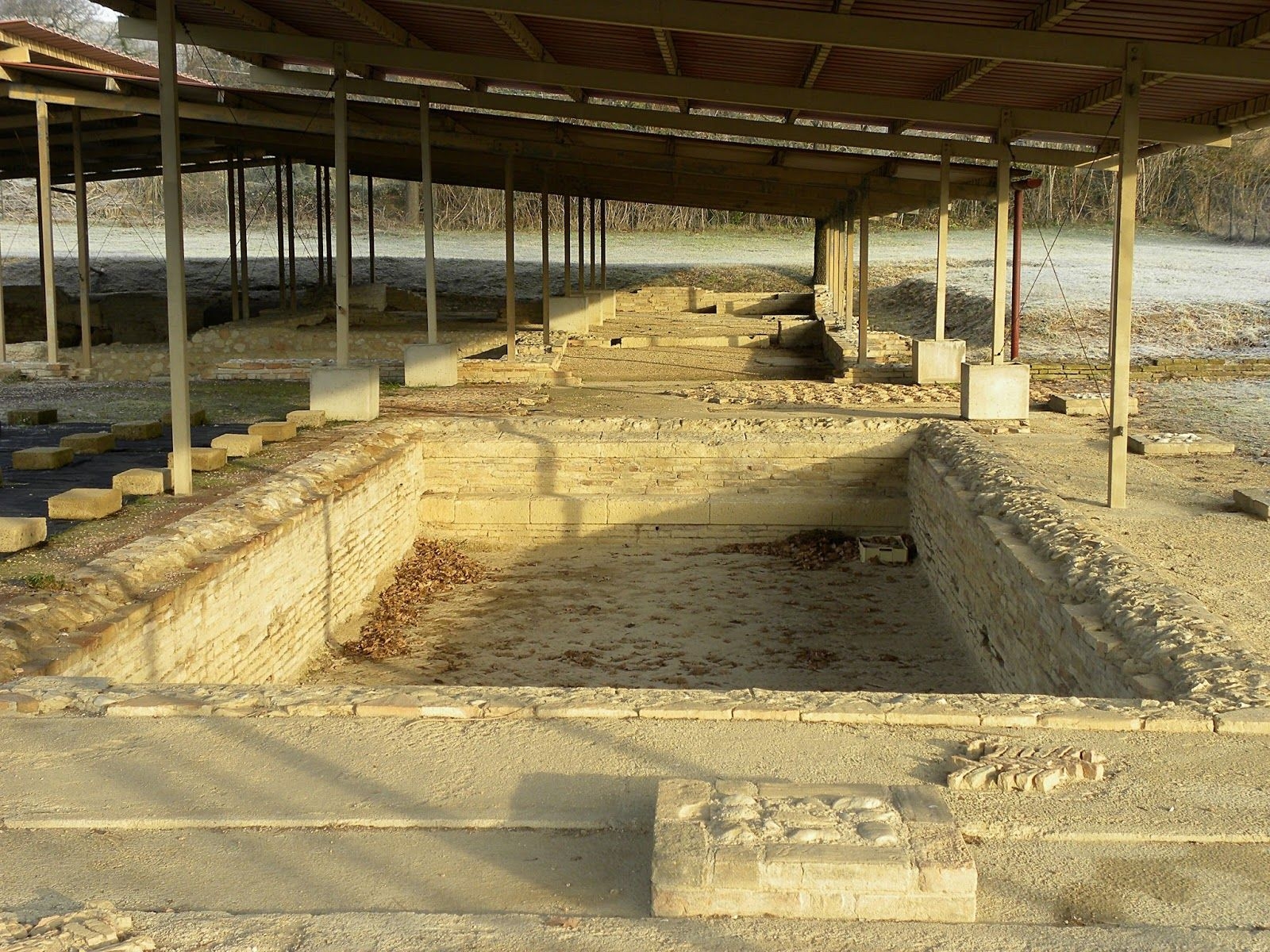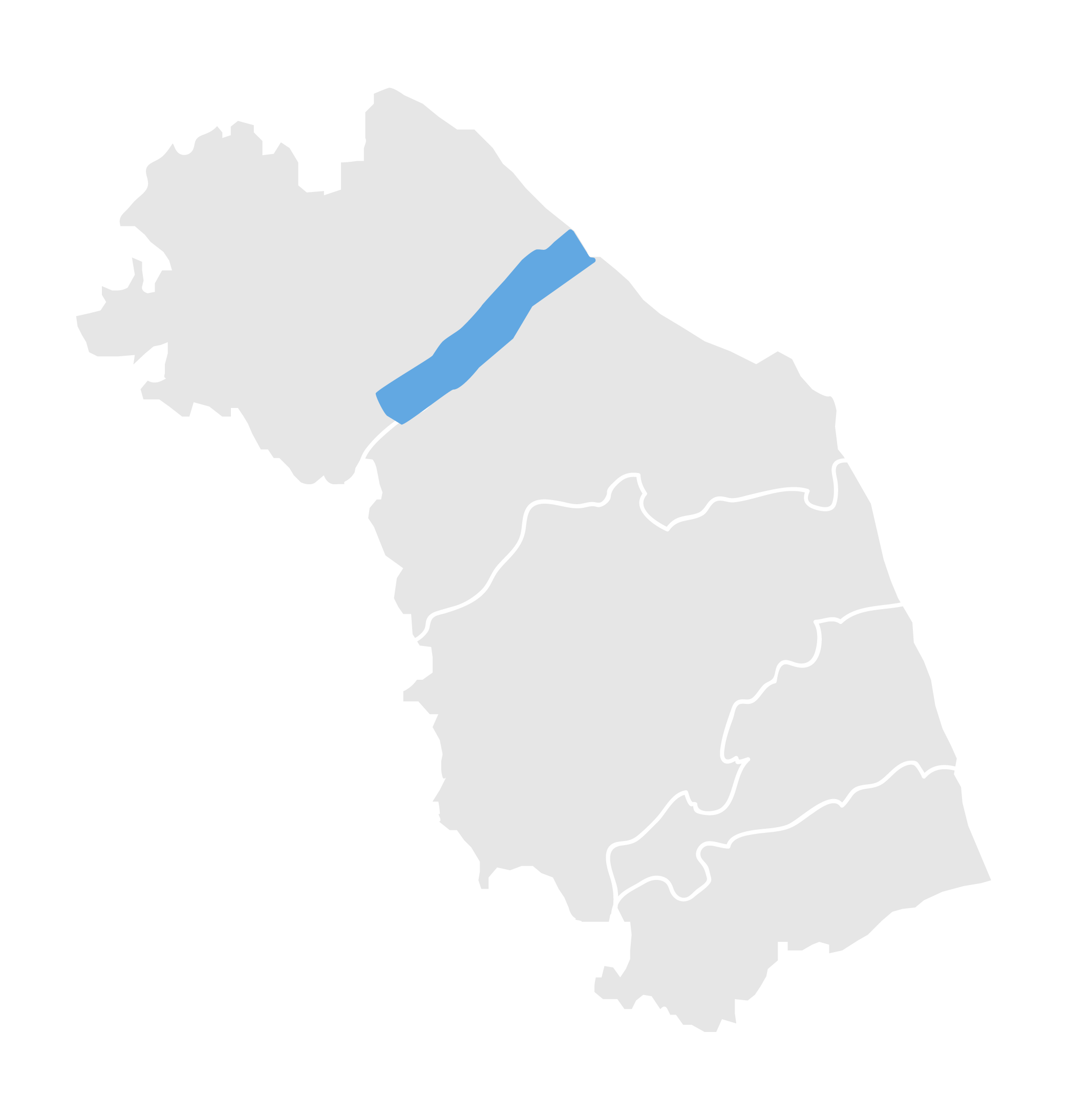
The ancient Roman city of Suasa occupies a large plain located in the middle valley of the Cesano, on the right bank of the river, about 2 km from the current municipality of Castelleone di Suasa. The city stood along a stretch of road that, passing through the Sentinum basin, connected Rome to the coastal areas before the construction of Via Flaminia and its byway that from Ad Calem connected the consular road to the coastal road, crossing the territories located on the left bank of the Cesano. Another important route widely frequented in the pre-Roman Age, the Via Salaria Gallica, passed through Suasa increasing its strategic importance in the control of the territories. This route connected the Via Flaminia to the Via Salaria, passing through the main centers of the valleys: Forum Sempronii, Suasa, Ostra, Aesis, Ricina, Urbs Salvia, Falerio and Asculum. Early Roman activity in the area can be dated to the time following the Battle of Sentinum in 295 BC. With the distribution to the Roman colonists of the territories taken from the Senones of Gallia, Suasa became the administrative center of the Cesano's middle valley. In the second half of the 1st century BC the city acquired the status of municipium, followed by a period of great prosperity that peaked in the 2nd century AD, when homes were built and the public buildings were monumentalized: the theater, the amphitheater and the forum. The 4th century AD saw the beginning of a gradual economic and urban decline that led to the total abandonment of the city between the 5th and 6th centuries AD. The entrance to the archaeological park is located in the museum area of the Domus of the Coiedii, where the ticket office is set up. The ancient Roman town of Suasa, today visitable over an area of about 10 hectares, is located along the valley road that from Castelleone di Suasa leads to Corinaldo and traces the ancient Roman route that was the Decumanus Maximus of the ancient city. This road, paved with slabs of local sandstone, was flanked by terracotta pavements with tiles in a herring-bone pattern. Along this road two necropolis areas have been identified, one to the north and the other to the south. Walking along the road from north to south, on the left is the Domus dei Coiedii, a large and luxurious private home situated between the forum and the amphitheater. This area, in the middle and late Republican Age (2nd c. BC - mid-1st c. AD), was occupied by several housing units; the one located in the northwest corresponded to the original nucleus of the domus. This small house, at the beginning of the 2nd century AD, was enlarged to become a large residential complex with terracotta tiled service environments, formal halls decorated with wall paintings, now preserved in the "A. Casagrande” Archaeological Civic Museum in Castelleone di Suasa, floors in mosaic and imported polychrome marbles. From the 3rd century AD there began a progressive decline in the structure, which led to its definitive abandonment towards the middle of 6th century AD. Continuing to the south, one can see the Casa del Primo Stile , which was built in the middle of the 2nd century BC and abandoned prematurely during the first half of the 1st century AD. On the right side of the road, in front of the Domus dei Coiedii, there is the forum area. In this area, the remains of two buildings were found, dating back to the 2nd and 1st century BC: one with a circular layout and the other rectangular. These remains once constituted the sacred nucleus of the city, later demolished for the construction of the portico and the tabernae (shops). The forum, built around the first half of the 1st century BC, is basically formed by a wide open area defined on three sides by a sequence of tabernae, open on a portico overlooking the square. Leaving the road and going behind the Domus dei Coiedii, one encounters the Suasa amphitheater, with eight vaulted entrances, two of which lead directly into the arena.
We have found no place to eat in the vicinity
We have found no place to sleep in the vicinity
Vino e olio, eccellenze dell’agricoltura e della gastronomia marchigiana, sono da sempre al centro dell’economia e dell’identità culturale locale, come testimoniano i numerosi impianti per la produzione olearia e vinicola presenti sin dall’età picena nella regione. Il viaggio alla scoperta del territorio dedicato all’antica produzione dell’olio e del vino ci conduce lungo la Salaria Gallica, strada che collegava Fossombrone ad Ascoli Piceno passando per le principali colonie romane, immerse nelle verdi colline marchigiane.
Da sempre luogo di incontro di varie culture, l’Ager Gallicus è il territorio marchigiano compreso tra l’Esino e il confine settentrionale della regione, così denominato dai romani in quanto occupato sin dalla fine del IV sec. a.C. dalla tribù celtica dei Galli Senoni. In questo contesto nel 295 a.C. si consumò una delle battaglie fondamentali della storia romana, avvenuta a Sentinum, che ha determinato le sorti dell’occupazione romana fino alla costa adriatica. Attraverso i siti e i Musei Archeologici di questi territorio verrete a contatto con le diverse civiltà che vi hanno convissuto intrecciando stretti legami culturali e mercantili.
Da sempre luogo di incontro di varie culture, l’Ager Gallicus è il territorio marchigiano compreso tra l’Esino e il confine settentrionale della regione, così denominato dai romani in quanto occupato sin dalla fine del IV sec. a.C. dalla tribù celtica dei Galli Senoni. In questo contesto nel 295 a.C. si consumò una delle battaglie fondamentali della storia romana, avvenuta a Sentinum, che ha determinato le sorti dell’occupazione romana fino alla costa adriatica. Attraverso i siti e i Musei Archeologici di questi territorio verrete a contatto con le diverse civiltà che vi hanno convissuto intrecciando stretti legami culturali e mercantili.

|
Address | Contrada Pian Volpello Castelleone di Suasa |

|
Phone Number | 3335351396 |
|
Opening Time | settembre-giugno: sabato e domenica 15:30-19:30; luglio-agosto: martedì, mercoledì, giovedì, venerdì, sabato e domenica: 16:00-20:00 |
|
Visit Time | 1 h e 30 min |
|
Entrance Fee | Intero: 5 € Ridotto per gruppi maggiori di 30 persone e scolaresche: 2 € Gratuità secondo legge |

|
Reservation Required | Prenotazione obbligatoria nel periodo invernale con almeno tre giorni di anticipo |

|
Bookshop | si |

|
Free Guided Tour | no |
|
Guided Tour | si, su prenotazione |
|
Parking | si |

|
Disabled Accessibility | si |

|
Audioguide | si |
|
Didactic Rooms | no |
|
Conference room | no |

|
English language | si |

|
Public Transport | no |

|
Family Services | no |

















